Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
The Lugano classification is used to stage lymphoma. There are 4 stages. Or these can be simplified into limited (early) or advanced stage.
There are different staging systems for skin lymphoma and childhood NHL. If your child has NHL, ask your specialist to explain their stage.
Read about skin lymphoma and the different stages
Doctors look at whether the lymphoma is:
on one side, or both sides of your
inside or outside the
They also look at the size of the lymphoma.
They do this by carrying out various tests, such as a or .
The diaphragm (pronounced dia-fram) is the big breathing muscle that separates the chest from the tummy (abdominal) area.
Doctors use the diaphragm as a guide because it is about halfway down the body.
Doctors look at whether your lymphoma is affecting your and organs inside the lymphatic system. These are called lymphatic sites. If it is affecting areas outside the lymphatic system they are called extranodal sites.
Lymphatic sites include a group of lymph nodes or an organ in the lymphatic system, such as the:
tonsils
Extranodal sites are sometimes called extralymphatic sites. They are outside the lymphatic system and include the:
lungs
liver
blood
kidneys
brain
Your doctor may use the letter E (for extranodal) after the stage number if you have lymphoma outside the lymphatic system. For example stage 1E. Your doctor or nurse can explain what this means for you.

This means that you have areas of lymphoma that measure above a certain size. The exact measurement depends on your type of NHL.
For example, in follicular lymphoma, bulky disease measures over 6 cm. In diffuse large B cell lymphoma, bulky disease is usually greater than 10 cm.
This means that you have one of the following:
lymphoma in a single lymph node or one group of lymph nodes, or an organ of the lymphatic system (such as the thymus)
lymphoma in an extranodal site (this is called stage 1E)
Below is an example of stage 1 lymphoma.
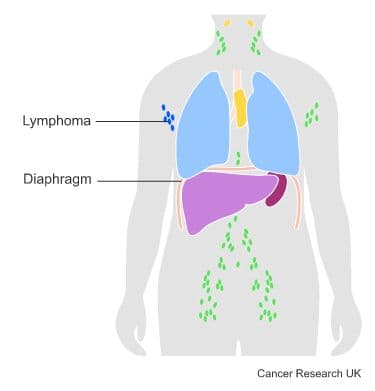
This means one of the following:
your lymphoma is in two or more groups of lymph nodes
your lymphoma is in an extranodal site and one or more groups of lymph nodes (this is called stage 2E)
In both cases, the 2 sites of lymphoma are on the same side of the diaphragm.
Below is an example of stage 2.

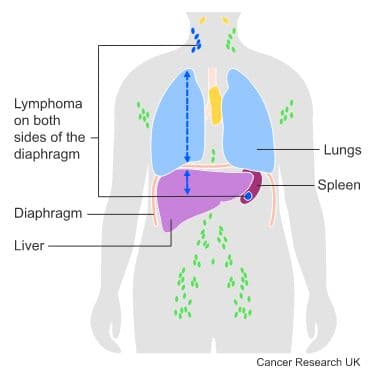
This means that you have lymphoma on both sides of the diaphragm.
Below is an example of stage 3. The lymphoma is in lymph nodes above the diaphragm and the spleen.
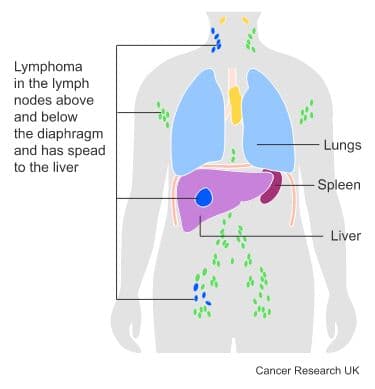
Stage 4 means one of the following:
lymphoma is in the lymph nodes and an extranodal site
lymphoma is in more than one extranodal site, for example the liver, bones or lungs
Below is an example of stage 4 lymphoma.
Your doctor may describe your lymphoma as being:
limited or early stage
advanced stage
Limited disease generally means you have stage 1 or stage 2 NHL. Doctors also call this early stage NHL.
Advanced disease means you have stage 3 or stage 4 NHL.
Some people with stage 2 bulky lymphoma might have advanced disease, depending on their circumstances.
You doctor or specialist nurse can explain what stage you have and what this means in your situation.
The stage of your lymphoma helps your doctor to decide which treatment you need. Your treatment also depends on:
the type of lymphoma you have
whether your lymphoma is slow growing (low grade) or fast growing (high grade)
where the lymphoma is in your body (the stage)
your symptoms
other health conditions that you have
your age
The main types of treatment for NHL are:
and drugs
Other treatments include:
surgery
You may have just one type of treatment or a combination of treatments.
Some people with NHL might not need treatment straight away. They have regular check ups instead. This is called watch and wait or active monitoring.
We have information about treatment for some of the different types of NHL.
Last reviewed: 25 Apr 2024
Next review due: 25 Dec 2027
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a type of blood cancer that affects white blood cells called lymphocytes. It's the 7th most common type of cancer in adults.
You usually start by seeing your GP. They might refer you to a specialist doctor (haematologist) and organise tests.
Your treatment depends on the type and stage of your NHL. Common treatments include chemotherapy, targeted and immunotherapy drugs, radiotherapy and a stem cell transplant.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a cancer of the lymphatic system. There are more than 60 different types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. They can behave in very different ways and need different treatments.

About Cancer generously supported by Dangoor Education since 2010. Learn more about Dangoor Education
Search our clinical trials database for all cancer trials and studies recruiting in the UK.
Connect with other people affected by cancer and share your experiences.
Questions about cancer? Call freephone 0808 800 40 40 from 9 to 5 - Monday to Friday. Alternatively, you can email us.